| Volltext anzeigen | |
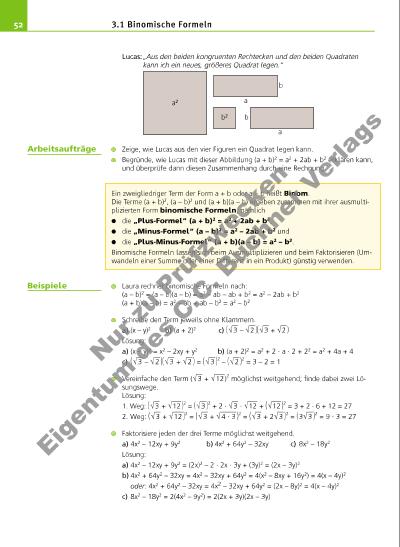
533.1 Binomische Formeln Vereinfache den Bruchterm T(x) = 0,5x 2 – 0,2x + 0,02 _______________ 0,5x2 – 0,02 ; x ± 0,2, durch Kürzen so weit wie möglich und berechne dann auf zwei Arten den Termwert für x = – 1. Lösung T(x) = 0,5x 2 – 0,2x + 0,02 _______________ 0,5x2 – 0,02 = 0,5(x 2 – 0,4x + 0,04) ________________ 0,5(x2 – 0,04) = (x – 0,2) 2 _____________ (x + 0,2)(x – 0,2) = x – 0,2 ______ x + 0,2 ; x ± 0,2 1. Art: T(– 1) = 0,5 · (– 1) 2 – 0,2 · (– 1) + 0,02 ______________________ 0,5 · (– 1)2 – 0,02 = 0,5 + 0,2 + 0,02 _____________ 0,5 – 0,02 = 0,72 ____ 0,48 = 1 1 __ 2 2. Art: T(– 1) = – 1 – 0,2 _______ – 1 + 0,2 = – 1,2 ____ – 0,8 = 1 1 __ 2 Erweitere jeden der beiden Bruchterme 5 ________ √ __ 5 – √ __ 3 und 8 ______ √ __ 7 + 2 so, dass dann im Nenner eine natürliche Zahl steht. Lösung (Rationalmachen des Nenners): 5 ________ √ __ 5 – √ __ 3 = 5( √ __ 5 + √ __ 3 ) ________________ ( √ __ 5 – √ __ 3 )( √ __ 5 + √ __ 3 ) = 5( √ __ 5 + √ __ 3 )___________ ( √ __ 5 )2 – ( √ __ 3 )2 = 5( √ __ 5 + √ __ 3 )__________ 5 – 3 = 5( √ __ 5 + √ __ 3 )__________ 2 8 ______ √ __ 7 + 2 = 8( √ __ 7 – 2) _____________ ( √ __ 7 + 2)( √ __ 7 – 2) = 8( √ __ 7 – 2) ________ ( √ __ 7 )2 – 22 = 8( √ __ 7 – 2) ________ 7 – 4 = 8( √ __ 7 – 2) ________ 3 Ermittle die Nullstellen der beiden Funktionen f1 und f2 mit f1(x) = (x – 7) 2 und f2(x) = x 2 – 16; Df1 = Df2 = + 0 . Lösung: f1(7) = 0; 7 X Df1 , also ist x = 7 (die einzige) Nullstelle von f1 . f2(x) = (x + 4)(x – 4); f2(– 4) = f2(4) = 0; wegen 4 X Df2 und – 4 x Df2 besitzt f2 (nur) die Nullstelle x1 = 4. Vergleiche die ausmultiplizierte Form der Terme (a – b)2 und (b – a)2. Finde Zahlen a und b so, dass ausnahmsweise (a + b)2 = a2 + b2 gilt. Finde Zahlen a und b so, dass ausnahmsweise (a – b)2 = a2 – b2 gilt. 1. Löse die Klammern mithilfe binomischer Formeln auf. a) (x + 1)2 b) (x + 2)2 c) (2x + 1)2 d) (2x + 0,5)2 e) (a – 5)2 f) (2b – 3)2 g) (0,5z – 4)2 h) (– 3x + 4)2 i) (2p + q)(2p – q) j) (3x – 0,5)(3x + 0,5) k) (– x + y)(x + y) l) (1 + 3z)(1 – 3z) m) ( 2 __ x – x __ 2 ) 2; x 0 n) ( 6a2 + 2 __ a ) 2; a 0 o) ( 1 __ x – x ) ( 1 __ x + x ) ; x 0 p) (b + a)2 – (b – a)2 2. Berechne jeweils den Termwert mit dem Taschenrechner und exakt. a) ( √ __ 6 + √ __ 3 ) · ( √ __ 6 – √ __ 3 ) b) ( √ __ 6 – 2 √ __ 3 ) 2 c) ( √ __ 6 + √ __ 3 ) 2 d) ( √ __ 2 – √ __ 8 ) 2 e) ( √ __ 7 + √ __ 2 ) ( √ __ 7 – √ __ 2 ) f) ( √ __ 7 + √ __ 2 ) 2 g) ( √ __ 7 – √ __ 2 ) 2 h) ( √ __ 2 + 1 ___ √ __ 2 ) 2 i) ( √ __ 8 – √ __ 5 ) ( √ __ 5 + √ __ 8 ) j) ( √ __ 8 + √ __ 2 ) 2 k) ( 2 √ __ 3 – √ __ 6 ) 2 3. Löse die Klammern mithilfe binomischer Formeln auf und erkläre deine Beobachtung. a) (x – 2)2 und (2 – x)2 b) (x + 2)2 und (– x – 2)2 c) (5s – 3t)2 und (3t – 5s)2 d) (5s + 3t)2 und (5t + 3s)2 e) ( √ __ 5 – √ __ 2 )2 und ( √ __ 2 – √ __ 5 )2 f) ( √ __ 3 + 3 √ __ 8 )2 und (3 √ __ 3 + √ __ 8 )2 18 – 12 √ __ 2 ; 9 – 2 √ ___ 14 ; 2; 3; 4,5; 5; 9 + 2 √ ___ 14 ; 9 + 6 √ __ 2 ; 18 Exakte Termwerte zu 2. Laura erinnert sich: Ein Produkt hat den Wert 0, wenn mindestens einer seiner Faktoren gleich 0 ist. L Es wurde mit √ __ 5 + √ __ 3 erweitert. Es wurde mit √ __ 7 – 2 erweitert. Aufgaben Nu r z u Pr üf zw ec ke n Ei ge nt um d es C .C . B uc hn er V rla gs | |
 « |  » |
|
» Zur Flash-Version des Livebooks | |